Difference between revisions of "The Data Dump Paper"
From Ucsbgalaxy
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
====H1: Pleiotropy==== | ====H1: Pleiotropy==== | ||
Molecular components are shared between chemo- and photo-reception. Do opsins artifactually affect the chemo-transduction cascade? | Molecular components are shared between chemo- and photo-reception. Do opsins artifactually affect the chemo-transduction cascade? | ||
| + | * Background | ||
| + | ** Known cnidarian phototransduction systems use G-alpha-s, which may stimulate adenylyl cyclase (AC) to decrease cAMP, | ||
| + | ** In ''Haliplanella'', NANA may signal an unknown receptor that activates G-alpha-s, which may stimulate AC to decrease cAMP, which lengthens hair bundles to tune nematocyte firing to lower frequency vibrations. | ||
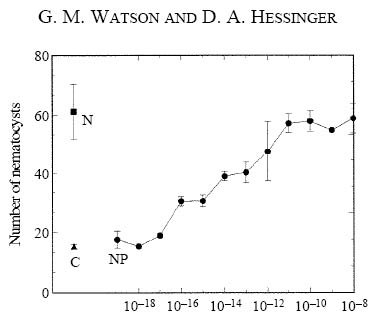
| + | ** Watson and Hessinger proposed that proline acts in opposition to NANA, and its receptor signals through G-alpha-i to shorten hair bundles and tune firing to higher frequency vibrations. | ||
| + | [[File:WatsonPtxExperiment.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
* Katia tested effects of light and mucin together on nematocyte firing. | * Katia tested effects of light and mucin together on nematocyte firing. | ||
* Federico tested whether light sensitivity involves G-alpha-i by using Pertussis toxin | * Federico tested whether light sensitivity involves G-alpha-i by using Pertussis toxin | ||
| + | |||
====H2: Light cues signal reliability of different feeding modes==== | ====H2: Light cues signal reliability of different feeding modes==== | ||
* Bright light could favor transition to relying on photosynthetic symbionts. | * Bright light could favor transition to relying on photosynthetic symbionts. | ||
| − | * Dim light could signal nightfall, | + | * Dim light could signal nightfall, when zooplankton prey are more active |
==Methods== | ==Methods== | ||
Revision as of 12:53, 22 November 2011
Contents
Title
Abstract
Introduction
Question 1 - Is Light Modulation Ancestral in Cnidaria?
- Previous research indicates light modulates nematocyte firing in hydra. See Plachetzki nematocyte firing.
- Do cnidarians from other classes show a similar response to light, with respect to the modulation of nematocyte firing?
- In addition to the hydrozoan hydra, we tested light modulation of nematocyte firing in one scyphozoan (Aureila), and two anthozoans (Anthopleura and Haliplanella).
Question 2 - Why Light modulation?
H1: Pleiotropy
Molecular components are shared between chemo- and photo-reception. Do opsins artifactually affect the chemo-transduction cascade?
- Background
- Known cnidarian phototransduction systems use G-alpha-s, which may stimulate adenylyl cyclase (AC) to decrease cAMP,
- In Haliplanella, NANA may signal an unknown receptor that activates G-alpha-s, which may stimulate AC to decrease cAMP, which lengthens hair bundles to tune nematocyte firing to lower frequency vibrations.
- Watson and Hessinger proposed that proline acts in opposition to NANA, and its receptor signals through G-alpha-i to shorten hair bundles and tune firing to higher frequency vibrations.
- Katia tested effects of light and mucin together on nematocyte firing.
- Federico tested whether light sensitivity involves G-alpha-i by using Pertussis toxin
H2: Light cues signal reliability of different feeding modes
- Bright light could favor transition to relying on photosynthetic symbionts.
- Dim light could signal nightfall, when zooplankton prey are more active